Using GraphQL Index API
Index API Documentation
Section titled “Index API Documentation”Overview
Section titled “Overview”The public API includes mutations:
- index mutation for creating or updating a document
- bulkIndex mutation for creating or updating multiple document
- delete mutation for deleting a document
- deleteAll mutation for deleting all documents
To use a mutation, you need to authenticate.
Authentication
Section titled “Authentication”Clients calling the API mutations are required to add an authentication header with the valid authentication token.
Authorization: Bearer {ACCESS_TOKEN}Data needed to consume API can be found in your WP Admin area in the WP Engine Smart Search tab under Settings.
Creating or Updating a Document
Section titled “Creating or Updating a Document”To create or update a document in the index using the mutation, you need to:
- Use the
indexmutation. - Provide a
DocumentInputobject as a parameter. - In the
DocumentInputobject, provide the necessary document data as aJSONobject. - To ensure a document has a unique identifier in the
DocumentInputobject, follow these guidelines:- The
idfield of theDocumentInputobject should be used to provide a unique identifier for the document. This field is required for updating a document. - If an
idis provided in theDocumentInputobject, the system checks whether a document with thatidalready exists. If it does, the existing document is updated with the new data instead of creating a new document. - In cases where no
idis provided in theDocumentInputobject, the system automatically generates a unique identifier for the document. This ensures that each document has a unique identifier, even if one is not explicitly provided. By following these guidelines, you can effectively handle document creation and updates, ensuring uniqueness of identifiers and appropriate handling based on the presence of anidin theDocumentInputobject. - The
datafield is required and contains all the index data.
- The
- Optionally, you can include metadata by using the
metafield. This allows you to provide additional information that will be logged on the server. Metadata can be helpful for analyzing and understanding the logs more effectively. Meta data includes optional fields:system- should be the name of the client “Atlas Search v0.2.24”action- the name of the action performed e. g. “manual-index”source- hostname from where action has been performed e. g. “atlasce.wpengine.com”
GraphQL example to create a document
Section titled “GraphQL example to create a document”mutation CreateIndexDocument($input: DocumentInput!) { index(input: $input) { success code message document { id data } }}GraphQL Variables
{ "input": { "data": { "ID": 1, "post_title": "Post Title", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt", "post_content": "Post Content", "post_date": "11-06-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" }, "meta": { "system": "Atlas Search v0.2.24", "action": "manual-index", "source": "cms.themessenger.com" } }}Mutation Response
{ "data": { "index": { "success": true, "code": "200", "message": "Document was indexed successfully", "document": { "id": "yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh", "data": { "ID": 1, "post_title": "Post Title", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt", "post_content": "Post Content", "post_date": "11-06-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" } } } }}In this example, we’re creating a new document with fields: ID, post_title, post_excerpt, post_content, post_date, post_type, post_status. The mutation returns a DocumentMutationResponse object that includes fields:
success- a boolean says if operation is successful or notcode- string with number of response code (200 - is success)message- human readable operation statusdocumentwithidanddata.
To create a new document with a provided id or update an existing document, you can use the index mutation. The behavior depends on whether a document with the provided id already exists:
- If a document with the provided
iddoesn’t exist, a new document will be created with the specifiedid. - If a document with the provided
idalready exists, the existing document will be updated with the new data.
To create a new document with a provided id or update an existing document, you need to provide the id of the document you want to update in the DocumentInput object.
GraphQL example to update a document
Section titled “GraphQL example to update a document”mutation UpdateIndexDocument($input: DocumentInput!) { index(input: $input) { success code message document { id data } }}GraphQL Variables
{ "input": { "id": "yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh", "data": { "post_title": "Post with updated title" }, "meta": { "system": "Atlas Search v0.2.24", "action": "manual-index", "source": "cms.themessenger.com" } }}Mutation Response
{ "data": { "index": { "success": true, "code": "200", "message": "Document was indexed successfully", "document": { "id": "yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh", "data": { "post_title": "Post with updated title" } } } }}In this example, we’re updating an existing document with the id of yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh. We are mutating post_title field of the document. The mutation returns a DocumentMutationResponse object.
The same behavior would occur even if the document did not already exist. In that case, it would be created with the provided id and the DocumentMutationResponse would include this id.
Indexing third party data
Section titled “Indexing third party data”It is recommended to have a data structure to tag third party data so that it can be filtered later if needed. Otherwise, by default, the search query considers every document in the index.
To index third party data, provision a WP environment with smart search. Then, by using the url and access_token found on the WP Smart Search settings page, configure the third party data client with these credentials and then calling the index API.
Once the application is running the headless app, use the find api to query for documents held in the index.
The only way to obtain a license at the moment is to purchase a plan that has the smart-search entitlement.
Code sample
Section titled “Code sample”The following is an example written in javascript which queries a “space” endpoint and indexes the first record via the WP Engine Smart Search API.
const spaceUrl = 'https://www.space.com/api/product_search?first_edition=true&ship_to_country=USA&minimum_price=50';const spaceHeaders = { 'X-API-KEY': 'YOUR_SPACE_API_KEY',};const spacePayload = { method: 'GET', headers: spaceHeaders,};const smartSearchEndpoint = 'YOUR_SMART_SEARCH_URL';const smartSearchHeaders = { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_SMART_SEARCH_TOKEN',};
// First lets fetch data from the space endpointfetch(spaceUrl, spacePayload) .then((response) => response.json()) .then((data) => { // Here lets get the first document returned in the response const firstDocument = data.data[0]; // lets image the data structure is the following // { "id": 12345, "title": "hello" } // lets create a custom id by prepending 'space:' const documentId = `space:${firstDocument.id}`; // assign our variables for the index request
// add space as the root of the document const variables = { input: { id: documentId, data: { space: firstDocument, }, }, }; // This is the graphql mutation for indexing documents // a link to the API documentation can be found at the top // of this document const mutation = ` mutation CreateIndexDocument($input: DocumentInput!) { index(input: $input) { success code message document { id data } } } `; const payload = { method: 'POST', headers: smartSearchHeaders, body: JSON.stringify({ query: mutation, variables: variables, }), }; // Send the GraphQL request which will index the first document return fetch(smartSearchEndpoint, payload); }) .then((response) => response.json()) .then((data) => { if (data.errors) { throw new Error(data.errors[0].message); } else { console.log(data); } }) .catch((error) => console.error('Error:', error));{ "post_title": "Star Wars", "post_contents": "Star Wars conent", "post_type": "metadata"}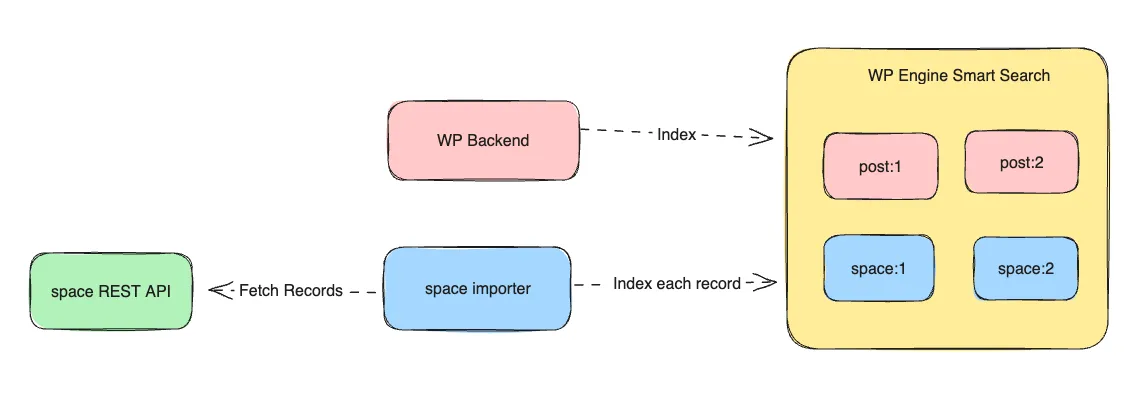
Sample query filtering for just metadata content
Section titled “Sample query filtering for just metadata content”query FindSimpleQuery { find(query: "Star Wars", filter: "post_type:metadata") { total documents { id data } }}These query appendages could happen under the hood or just considering all content
query FindSimpleQuery { find(query: "Star Wars", filter: "post_type:post,metadata") { total documents { id data } }}Creating or Updating multiple Documents
Section titled “Creating or Updating multiple Documents”To create or update multiple documents in one API call you need to:
- Use the
bulkIndexmutation. - Provide a
BulkIndexInputobject as a parameter. - In the
BulkIndexInputobject, provide the necessary document data as aJSONobject. - To ensure that each document has a unique identifier in the
BulkIndexInputobject, follow these guidelines:- The
idfield of aBulkIndexInputdocument object should be used to provide a unique identifier for each document. This field is required for updating a document. - If an
idis provided in theBulkIndexInputdocument object, the system checks whether a document with thatidalready exists. If it does, the existing document is updated with the new data instead of creating a new document. - In cases where no
idis provided in theBulkIndexInputdocument object, the system automatically generates a unique identifier for the document. This ensures that each document has a unique identifier, even if one is not explicitly provided. By following these guidelines, you can effectively handle document creation and updates, ensuring uniqueness of identifiers and appropriate handling based on the presence of anidin theDocumentInputobject. - The
datafield is required and contains all the index data.
- The
- Optionally, you can include metadata by using the
metafield. This allows you to provide additional information that will be logged on the server. Metadata can be helpful for analyzing and understanding the logs more effectively. Meta data includes optional fields:system- should be the name of the client “Atlas Search v0.2.24”action- the name of the action performed e. g. “manual-index”source- hostname from where action has been performed e. g. “atlasce.wpengine.com”
GraphQL example to create multiple documents
Section titled “GraphQL example to create multiple documents”mutation CreateBulkIndexDocuments($input: BulkIndexInput!) { bulkIndex(input: $input) { code success documents { id } }}GraphQL Variables
{ "input": { "documents": [ { "data": { "ID": 1, "post_title": "Post Title", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt", "post_content": "Post Content", "post_date": "11-06-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" } }, { "data": { "ID": 2, "post_title": "Post Title2", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt2", "post_content": "Post Content2", "post_date": "11-08-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" } } ] }}Mutation Response
{ "data": { "bulkIndex": { "code": "200", "success": true, "documents": [ { "id": "9932_pABTRDKaIXj6AyZ" }, { "id": "-N32_pABTRDKaIXj6AyZ" } ] } }}In this example, we’re creating two new documents with fields: ID, post_title, post_excerpt, post_content, post_date, post_type, post_status. The mutation returns a BulkIndexMutationResponse object that includes fields:
success- a boolean says if operation is successful or notcode- string with number of response code (200 - is success)message- human-readable operation statusdocumentwithid.
To create a new documents with a provided id or update an existing document, you can still use the bulkIndex mutation. The behavior depends on whether a document with the provided id already exists:
- If a document with the provided
iddoesn’t exist, a new document will be created with the specifiedid. - If a document with the provided
idalready exists, the existing document will be updated with the new data.
To create a new document with a provided id or update an existing document, you need to provide the id of the document you want to update in the BulkIndexInput object.
GraphQL example to update multiple documents
Section titled “GraphQL example to update multiple documents”mutation UpdateBulkIndexDocuments($input: BulkIndexInput!) { bulkIndex(input: $input) { code success documents { id } }}GraphQL Variables
{ "input": { "documents": [ { "id": "post:1", "data": { "ID": 1, "post_title": "Changed Post Title", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt", "post_content": "Post Content", "post_date": "11-06-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" } }, { "id": "post:2", "data": { "ID": 2, "post_title": "Changed Post Title2", "post_excerpt": "Post Excerpt2", "post_content": "Post Content2", "post_date": "11-08-2023T12:33:00", "post_type": "post", "post_status": "publish" } } ] }, "meta": { "system": "Atlas Search v0.2.24", "action": "manual-index", "source": "cms.themessenger.com" }}Mutation Response
{ "data": { "bulkIndex": { "code": "200", "success": true, "documents": [ { "id": "post:1" }, { "id": "post:2" } ] } }}In this example, we’re updating an existing documents with the ids of post:1, post:2. We are mutating post_title field of the document. The mutation returns a BulkIndexMutationResponse object.
The same behavior would occur even if a document did not already exist. In that case, it would be created with the provided id and the BulkIndexMutationResponse would include this id.
IMPORTANT Rest of the fields not specified in the input will be removed.
In this case it will remove ID, post_excerpt, post_content, post_date, post_type, post_status and only post_title will be added.
Deleting a Document
Section titled “Deleting a Document”To delete a document from the index, you need to:
- Use the
deletemutation. - Provide the
idof the document you want to delete. - Optionally provide metadata by using the
metafield. This allows you to provide additional information that will be logged on the server. Including metadata can be helpful for analyzing and understanding the logs more effectively. Meta data includes optional fields:system- should be the name of the client “Atlas Search v0.2.24”action- the name of the action performed e. g. “manual-index”source- hostname from where action has been performed e. g. “atlasce.wpengine.com”
GraphQL example to delete a document
Section titled “GraphQL example to delete a document”mutation deleteDocument($id: ID!, $meta: MetaInput) { delete(id: $id, meta: $meta) { code success message document { id data } }}GraphQL Variables
{ "id": "yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh", "meta": { "system": "Atlas Search v0.2.24", "action": "manual-delete", "source": "cms.themessenger.com" }}GraphQL Response
{ "data": { "delete": { "code": "200", "success": true, "message": "Document was deleted successfully", "document": { "id": "yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh", "data": {} } } }}We are deleting a document with the id of yMI9vogB0FEetE6QV9fh.
The mutation returns a DocumentMutationResponse object that includes the id and data fields of the deleted document.
Deleting All Documents
Section titled “Deleting All Documents”To delete all documents from the index you need to:
- Use
deleteAllmutation. - Optionally provide metadata by using the
metafield. This allows you to provide additional information that will be logged on the server. Including metadata can be helpful for analyzing and understanding the logs more effectively.
GraphQL Example to Delete All Documents
Section titled “GraphQL Example to Delete All Documents”mutation deleteAllDocuments($meta: MetaInput) { deleteAll(meta: $meta) { code success message }}GraphQL Variables
{ "meta": { "system": "Atlas Search v0.2.24", "action": "reset-data", "source": "cms.themessenger.com" }}GraphQL Response
{ "data": { "deleteAll": { "code": "200", "success": true, "message": "Delete all documents was successful" } }}